Network topology is the arrangement of the elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a communication network.
Network topology can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, including command and control radio networks, industrial fieldbusses and computer networks.
Type Of Network Topology
- Point to point topology.
- Bus topology.
- Ring topology.
- Star topology.
- Tree topology.
- Mesh topology.
- Hybrid topology.
- Daisy chain topology.
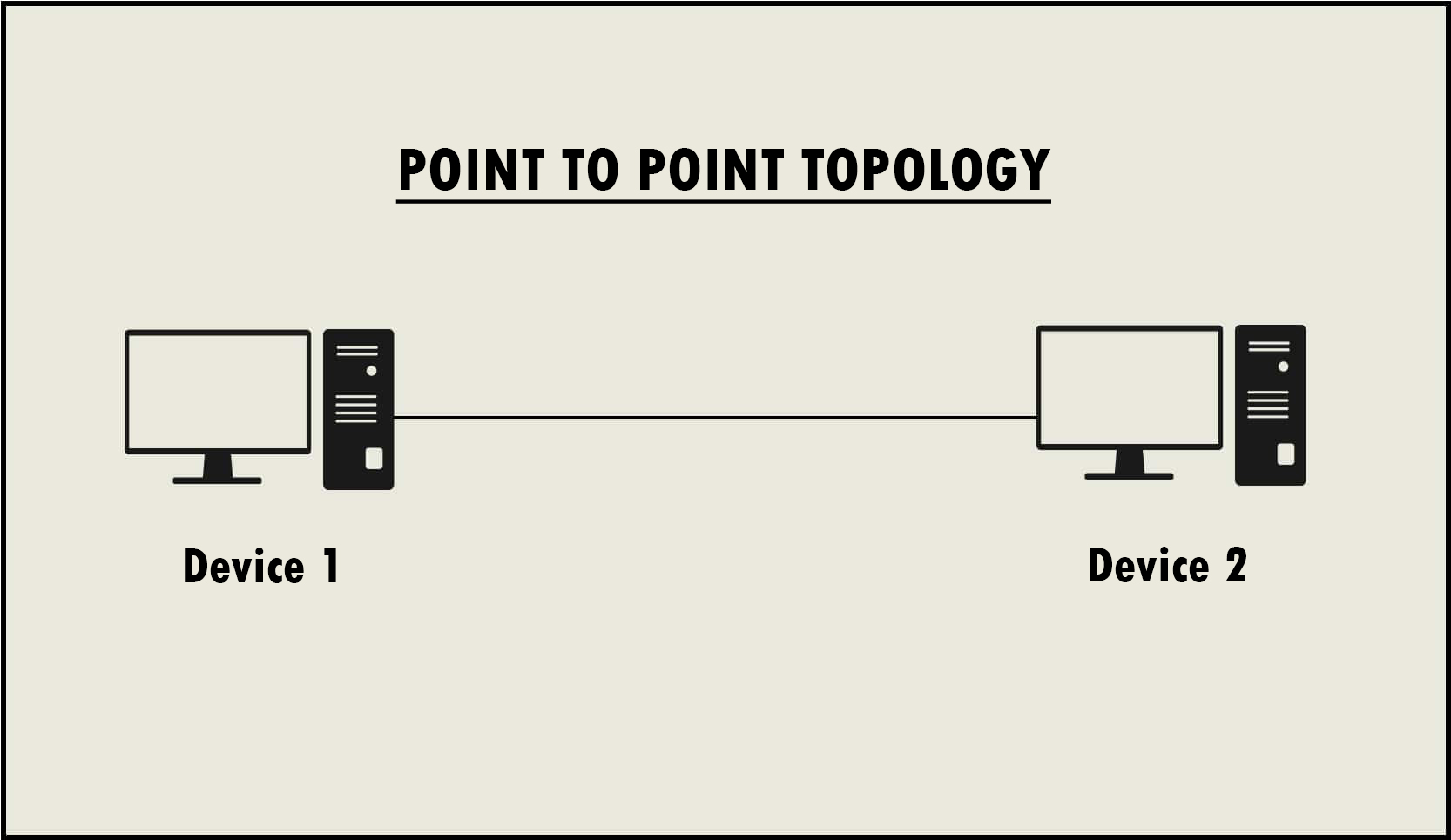
Point to point topology
A point-to-point topology is any network that connects two hosts in a dedicated fashion. For example, if you were to configure a router in Miami, Florida, to connect and use resources on a network in Atlanta, Georgia, you would want to make sure you had a link between them that can support your needs.
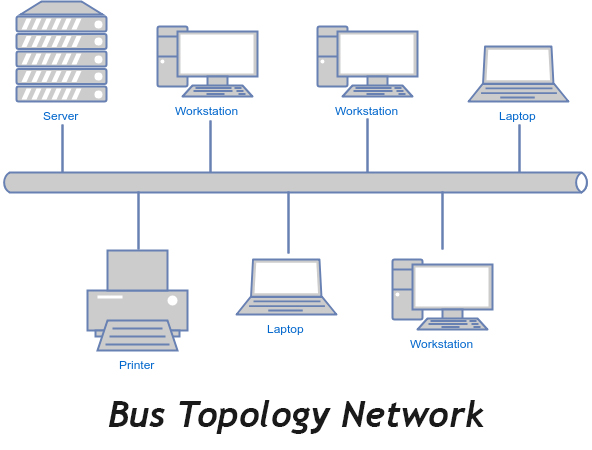
Bus topology
Bus topology, also known as line topology, is a type of network topology in which all devices in the network are connected by one central RJ-45 network cable or coaxial cable. The single cable, where all data is transmitted between devices, is referred to as the bus, backbone, or trunk.
Ring topology
Ring topology is a type of network topology in which each device is connected to two other devices on either side via an RJ-45 cable or coaxial cable. This forms a circular ring of connected devices which gives it its name. Data is commonly transferred in one direction along the ring, known as a unidirectional ring.
Star topology
Star topology is a type of network topology in which every device in the network is individually connected to a central node, known as the switch or hub. When represented visually, this topology resembles a star which gives it its name.
Tree topology
In computer networking, tree topology is a type of network topology that resembles a tree. In a tree topology, there is one central node (the “trunk”), and each node is connected to the central node through a single path. Nodes can be thought of as branches coming off of the trunk.
Mesh topology
Mesh topology is a type of network topology in which all devices in the network are interconnected. In a mesh topology, data can be transmitted by routing (sent the shortest distance) and flooding (sent to all devices).
The two types of mesh topology are:
- Full mesh topology. Every device in the network is connected to all other devices in the network. A full mesh offers high levels of redundancy but is expensive to implement. As such, it’s typically used for network backbones.
- Partial mesh topology. Only some of the devices in the network are connected to multiple other devices in the network. A partial mesh is more practical and cost-effective than a full mesh, and is more widely used.
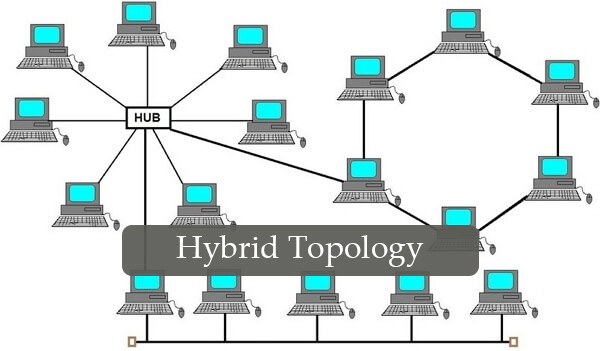
Hybrid topology
It is the combination of two or more different topologies. For example, in a college we have so many departments, let us say one department uses ring topology and another department uses Star topology, connecting these two topologies which results in Hybrid Topology.
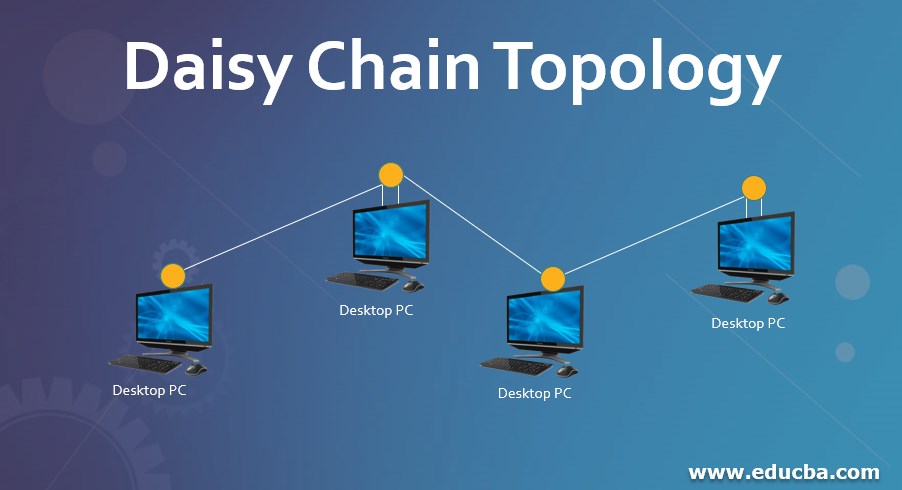
Daisy chain topology
A daisy chain is a type of network topology that directs how network nodes – typically, computers – are linked. Different network topologies support objectives, like ease of use, persistence and fault tolerant design.








0 Comments